Strands Agents 下篇 - Multi-Agent & A2A
深入探讨Strands Agents的三种多Agent交互模式:Swarm、Graph和Workflow。通过实战代码示例展示如何构建灵活的Agent协作系统,解决复杂任务编排和Agent间通信的挑战。
在上一篇文章中,我们介绍了如何使用Strands Agents SDK构建一个简单的A2A Server和Client进行通信,本篇讲构建Swarm、Graph和Workflow三种形式的A2A应用。
一、背景
1、A2A模式简介
Graph、Swarm和Workflow是Agent之间通信的三种行为方式,其中Graph和Swarm被集成在strands-agents的Python SDK中,而Workflow仅包含在strands-agents-tools的SDK中。前文的几个演示,我们同时安装了Python的这两个扩展,因此在使用方便不会有问题。
- Swarm:所有Agent之间都有通信能力,完全mesh的布局
- Graph:Agent之间的通信是有选择性的,Agent只和自己相关的一组Agent通信
- Workflow:Agent之间的通信是有顺序的,类似于流水线,前边的Agent不能跳过中间的Agent联系后边的Agent
三种模式对比:
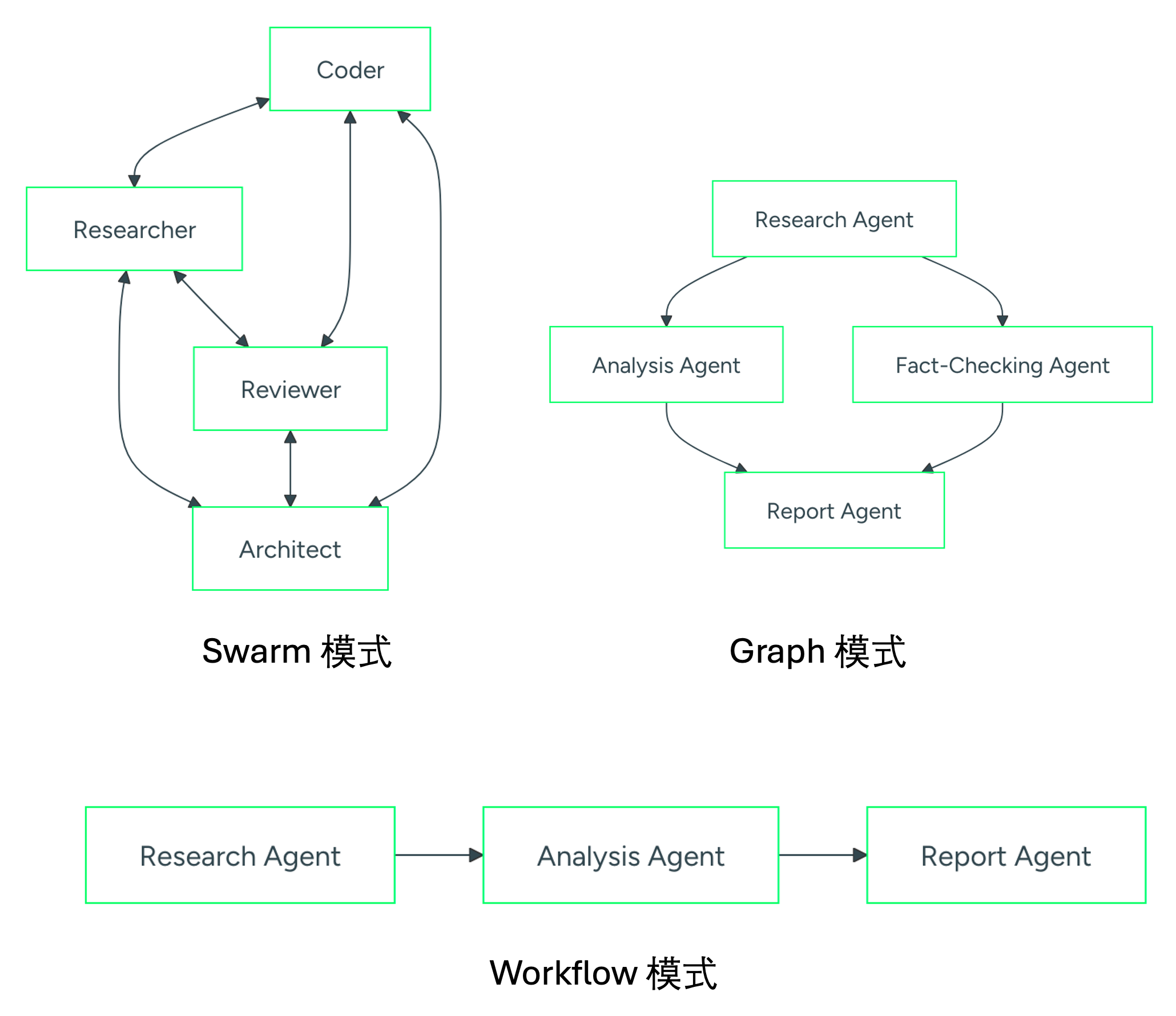
2、对比
以下对比表格来自Strands Agents的官方网站英文版翻译而成。
| 字段 | 图(Graph) | 群体(Swarm) | 工作流(Workflow) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 核心概念 | 结构化的、开发者定义的流程图,智能体决定采取哪条路径 | 动态的、协作的智能体团队,自主处理任务 | 预定义的任务图(DAG),作为单一的、非对话工具执行 |
| 结构 | 开发者预先定义所有节点(智能体)和边(转换) | 开发者提供智能体池。智能体自己决定路径 | 开发者在代码中定义所有任务及其依赖关系 |
| 执行流程 | 受控但动态。流程遵循图边,但每个节点的LLM决策决定路径 | 顺序和自主。智能体执行任务并使用工具将控制权传递给最合适的同伴 | 确定性和并行。流程由依赖图固定。独立任务并行运行 |
| 允许循环 | 是 | 是 | 否 |
| 状态共享机制 | 单一的共享字典对象传递给所有智能体,可以自由读取和修改 | “共享上下文"或工作内存对所有智能体可用,包含原始请求、任务历史和先前智能体的知识 | 工具自动捕获任务输出并将其作为输入传递给依赖任务 |
| 对话历史 | 完整记录。整个对话历史是共享状态的关键,为每个智能体提供完整和开放的上下文 | 共享记录。共享上下文提供智能体交接的完整历史和先前智能体贡献的知识,当前智能体可用 | 任务特定上下文。任务接收来自其依赖项的相关结果摘要,而非完整历史 |
| 行为控制 | 用户在每一步的输入可以直接影响图采取的下一条路径 | 用户的初始提示定义目标,但群体从那里自主运行 | 用户的提示可以触发预定义的工作流,但无法改变其内部结。 |
| 可扩展性 | 在处理复杂性方面扩展良好(许多分支、条件) | 随着团队中专业智能体数量和协作任务复杂性的增加而扩展 | 对可重复的复杂操作扩展良好 |
| 错误处理 | 可控制。开发者可以定义明确的"错误"边来路由流程,如果步骤失败,则路由到特定的错误处理节点 | 智能体驱动。智能体可以决定将错误交给错误处理专家。系统依赖智能体和交接限制来防止无限循环 | 系统性。一个任务的失败将停止所有下游依赖任务。整个工作流可能进入失败状态 |
下面我们逐个来测试。
二、Swarm模式例子
首先初始化环境。
uv init 06-swarm
cd 06-swarm
uv venv
source .venv/bin/activate
uv add strands-agents strands-agents-tools
将如下代码保存为swarm.py。内容如下。
import logging
from strands import Agent
from strands.multiagent import Swarm
from strands.models import BedrockModel
# 指定使用Amazon Bedrock上的特定模型版本、使用特定AWS Region
bedrock_model = BedrockModel(
model_id="us.anthropic.claude-sonnet-4-20250514-v1:0",
region_name="us-west-2"
)
# Enable debug logs and print them to stderr
logging.getLogger("strands.multiagent").setLevel(logging.DEBUG)
logging.basicConfig(
format="%(levelname)s | %(name)s | %(message)s",
handlers=[logging.StreamHandler()]
)
# Create specialized agents
researcher = Agent(name="researcher", model=bedrock_model, system_prompt="You are a research specialist...")
coder = Agent(name="coder", model=bedrock_model, system_prompt="You are a coding specialist...")
reviewer = Agent(name="reviewer", model=bedrock_model, system_prompt="You are a code review specialist...")
architect = Agent(name="architect", model=bedrock_model, system_prompt="You are a system architecture specialist...")
# Create a swarm with these agents, starting with the researcher
swarm = Swarm(
[researcher, coder, reviewer, architect],
#entry_point=architect, # Start with the researcher
max_handoffs=20,
max_iterations=20,
execution_timeout=900.0, # 15 minutes
node_timeout=300.0, # 5 minutes per agent
repetitive_handoff_detection_window=8, # There must be >= 3 unique agents in the last 8 handoffs
repetitive_handoff_min_unique_agents=3
)
# Execute the swarm on a task
result = swarm("Design and implement a simple REST API for a todo app")
# Access the final result
print(f"Status: {result.status}")
print(f"Node history: {[node.node_id for node in result.node_history]}")
# Get performance metrics
print("")
print(f"Total iterations: {result.execution_count}")
print(f"Execution time: {result.execution_time}ms")
print(f"Token usage: {result.accumulated_usage}")
运行后可以看到返回结果中,节选部分Agent交互的记录如下:
I'll help you design and implement a simple REST API for a todo app. Since this involves both architectural design and coding implementation, I'll hand this off to the architect first to create a solid design foundation.
Tool #1: handoff_to_agent
DEBUG | strands.multiagent.swarm | from_node=<researcher>, to_node=<architect> | handed off from agent to agent
DEBUG | strands.multiagent.swarm | node=<researcher> | node execution completed
DEBUG | strands.multiagent.swarm | current_node=<architect>, iteration=<2> | executing node
The task has been handed off to the architect who will design the system architecture for the todo app REST API. They'll define the data models, API endpoints, and overall structure before we proceed with implementation.
I'll design the architecture for a simple REST API for a todo app. Let me create a comprehensive system design that covers the data models, API endpoints, and overall structure.
## System Architecture Design
### 1. Data Model
在Architect Agent执行完毕后,日志中可以看到后续Agent的调用:
Now I'll hand off to the coder to implement this architecture:
Tool #1: handoff_to_agent
DEBUG | strands.multiagent.swarm | from_node=<architect>, to_node=<coder> | handed off from agent to agent
The architecture design is complete! I've provided a comprehensive system design that includes:
接着Coder Agenet会继续执行:
he coder willDEBUG | strands.multiagent.swarm | node=<architect> | node execution completed
DEBUG | strands.multiagent.swarm | current_node=<coder>, iteration=<3> | executing node
now implement this architecture and create a fully functional REST API. After implementation, the reviewer can validate that the code follows the architectural specifications and best practices.I'll implement a complete REST API for the todo app based on the architecture design provided. I'll use Python with Flask and SQLAlchemy for a clean, well-structured implementation.
## Todo REST API Implementation
都执行完毕后,将会返回:
This implementationDEBUG | strands.multiagent.swarm | node=<coder> | node execution completed
DEBUG | strands.multiagent.swarm | node=<coder> | no handoff occurred, marking swarm as complete
DEBUG | strands.multiagent.swarm | status=<Status.COMPLETED> | swarm execution completed
DEBUG | strands.multiagent.swarm | node_history_length=<3>, time=<78.33>s | metrics
provides a production-ready REST API for a todo application with all the architectural requirements fulfilled, including proper error handling, validation, and a clean, maintainable codebase.Status: Status.COMPLETED
Node history: ['researcher', 'architect', 'coder']
Total iterations: 3
Execution time: 78332ms
Token usage: {'inputTokens': 5571, 'outputTokens': 6054, 'totalTokens': 11625}
以上为Swarm模式的例子。
三、Graph模式
Graph模式是一组有特定顺序的编排,发起者可以是单个Agent也可以是多个,然后通过分支完成请求。所有的Agent被称为Node,它们之间的依存关系被称为Edge。不像在Swarm模式中所有Agent相对平等,Graph模式有着指定的执行路径,从指定的Entry Point启动,顺着Edge执行,并最终获得结果。
首先初始化环境。
uv init 07-graph
cd 07-graph
uv venv
source .venv/bin/activate
uv add strands-agents strands-agents-tools
将如下代码保存为graph.py。内容如下。
import logging
from strands import Agent
from strands.multiagent import GraphBuilder
from strands.models import BedrockModel
# Enable debug logs and print them to stderr
logging.getLogger("strands.multiagent").setLevel(logging.DEBUG)
logging.basicConfig(
format="%(levelname)s | %(name)s | %(message)s",
handlers=[logging.StreamHandler()]
)
# 指定使用Amazon Bedrock上的特定模型版本、使用特定AWS Region
bedrock_model = BedrockModel(
model_id="us.anthropic.claude-sonnet-4-20250514-v1:0",
region_name="us-west-2"
)
# Create specialized agents
researcher = Agent(name="researcher", model=bedrock_model, system_prompt="You are a research specialist...")
analyst = Agent(name="analyst", model=bedrock_model, system_prompt="You are a data analysis specialist...")
fact_checker = Agent(name="fact_checker", model=bedrock_model, system_prompt="You are a fact checking specialist...")
report_writer = Agent(name="report_writer", model=bedrock_model, system_prompt="You are a report writing specialist...")
# Build the graph
builder = GraphBuilder()
# 添加所有Agent节点
builder.add_node(researcher, "research")
builder.add_node(analyst, "analysis")
builder.add_node(fact_checker, "fact_check")
builder.add_node(report_writer, "report")
# 设置两两之间的关系
# entry point是research agent,然后分别交给analysis和fact_check
builder.add_edge("research", "analysis")
builder.add_edge("research", "fact_check")
# 在analysis和fact_check分别执行完毕后,结果汇总到report
builder.add_edge("analysis", "report")
builder.add_edge("fact_check", "report")
# Set entry points (optional - will be auto-detected if not specified)
builder.set_entry_point("research")
# Optional: Configure execution limits for safety
builder.set_execution_timeout(900) # 10 minute timeout
builder.set_node_timeout(600)
# Build the graph
graph = builder.build()
# Execute the graph on a task
result = graph("Research the impact of AI on healthcare and create a comprehensive report")
# Access the results
print(f"\nStatus: {result.status}")
print(f"Execution order: {[node.node_id for node in result.execution_order]}")
执行代码。
python graph.py
执行代码后,可看到如下日志输出,标识从research作为执行入口开始执行。
$ python graph.py
DEBUG | strands.multiagent.graph | task=<Research the impact of AI on healthcare and create a comprehensive report> | starting graph execution
DEBUG | strands.multiagent.graph | max_node_executions=<None>, execution_timeout=<600>s, node_timeout=<None>s | graph execution config
DEBUG | strands.multiagent.graph | node_id=<research> | executing node
Research执行完毕后,按照edge的定义,分别交给analysis agent和fact_check agent这两个分支执行。
ThisDEBUG | strands.multiagent.graph | node_id=<research>, execution_time=<41520ms> | node completed successfully
DEBUG | strands.multiagent.graph | from=<research>, to=<analysis> | edge ready via satisfied condition
DEBUG | strands.multiagent.graph | from=<research>, to=<fact_check> | edge ready via satisfied condition
DEBUG | strands.multiagent.graph | node_id=<analysis> | executing node
DEBUG | strands.multiagent.graph | node_id=<fact_check> | executing node
comprehensive report provides a balanced analysis of AI's impact on healthcare, addressing both opportunities and challenges while offering practical recommendations for various stakeholders in the healthcare ecosystem.# Data Analysis Report: AI Healthcare Impact Assessment
接下来日志中可看到fact_check agent执行完毕。
**DEBUG | strands.multiagent.graph | node_id=<fact_check>, execution_time=<10952ms> | node completed successfully
日志可看到analysis agent完成。
**DEBUG | strands.multiagent.graph | node_id=<analysis>, execution_time=<39515ms> | node completed successfully
DEBUG | strands.multiagent.graph | from=<analysis>, to=<report> | edge ready via satisfied condition
DEBUG | strands.multiagent.graph | node_id=<report> | executing node
Analysis Methodology Note:** This assessment utilized quantitative data analysis, trend analysis, comparative performance evaluation, and predictive modeling techniques to provide comprehensive impact assessment of AI in healthcare based on available research data and industry reports.# Comprehensive Report: The Impact of AI on Healthcare
最终report agent执行完毕。4个agent按时间顺序也分别打出。
*DEBUG | strands.multiagent.graph | node_id=<report>, execution_time=<56123ms> | node completed successfully
DEBUG | strands.multiagent.graph | status=<Status.COMPLETED> | graph execution completed
This report represents a comprehensive analysis based on current industry research, market data, and implementation experiences. Healthcare organizations should conduct specific assessments of their unique circumstances and requirements when developing AI implementation strategies.*
Status: Status.COMPLETED
Execution order: ['research', 'fact_check', 'analysis', 'report']
以上就是一个graph模式的A2A的例子。
四、Workflow模式
Workflow模式是针对复杂任务场景进行人工编排、对执行顺序有特别要求的场景。使用Strands Agents开发Workflow模式的Agent交互非常简单,无须人为的转发、传递参数,而是通过预设一个工作流即可完成。
首先初始化环境。
uv init 08-workflow
cd 08-workflow
uv venv
source .venv/bin/activate
uv add strands-agents strands-agents-tools
将如下代码保存为workflow.py。内容如下。
#!/usr/bin/env python3
"""
# Agentic Workflow: Research Assistant
This example demonstrates an agentic workflow using Strands agents with web research capabilities.
## Key Features
- Specialized agent roles working in sequence
- Direct passing of information between workflow stages
- Web research using http_request and retrieve tools
- Fact-checking and information synthesis
## How to Run
1. Navigate to the example directory
2. Run: python research_assistant.py
3. Enter queries or claims at the prompt
## Example Queries
- "Thomas Edison invented the light bulb"
- "Tuesday comes before Monday in the week"
## Workflow Process
1. Researcher Agent: Gathers web information using multiple tools
2. Analyst Agent: Verifies facts and synthesizes findings
3. Writer Agent: Creates final report
"""
from strands import Agent
from strands_tools import http_request
from strands.models import BedrockModel
# 指定使用Amazon Bedrock上的特定模型版本、使用特定AWS Region
bedrock_model = BedrockModel(
model_id="us.anthropic.claude-sonnet-4-20250514-v1:0",
region_name="us-west-2"
)
def run_research_workflow(user_input):
"""
Run a three-agent workflow for research and fact-checking with web sources.
Shows progress logs during execution but presents only the final report to the user.
Args:
user_input: Research query or claim to verify
Returns:
str: The final report from the Writer Agent
"""
print(f"\nProcessing: '{user_input}'")
# Step 1: Researcher Agent with enhanced web capabilities
print("\nStep 1: Researcher Agent gathering web information...")
researcher_agent = Agent(
system_prompt=(
"You are a Researcher Agent that gathers information from the web. "
"1. Determine if the input is a research query or factual claim "
"2. Use your research tools (http_request, retrieve) to find relevant information "
"3. Include source URLs and keep findings under 500 words"
),
model=bedrock_model,
callback_handler=None,
tools=[http_request]
)
researcher_response = researcher_agent(
f"Research: '{user_input}'. Use your available tools to gather information from reliable sources. "
f"Focus on being concise and thorough, but limit web requests to 1-2 sources.",
)
# Extract only the relevant content from the researcher response
research_findings = str(researcher_response)
print("Research complete")
print("Passing research findings to Analyst Agent...\n")
# Step 2: Analyst Agent to verify facts
print("Step 2: Analyst Agent analyzing findings...")
analyst_agent = Agent(
system_prompt=(
"You are an Analyst Agent that verifies information. "
"1. For factual claims: Rate accuracy from 1-5 and correct if needed "
"2. For research queries: Identify 3-5 key insights "
"3. Evaluate source reliability and keep analysis under 400 words"
),
model=bedrock_model,
callback_handler=None
)
analyst_response = analyst_agent(
f"Analyze these findings about '{user_input}':\n\n{research_findings}",
)
# Extract only the relevant content from the analyst response
analysis = str(analyst_response)
print("Analysis complete")
print("Passing analysis to Writer Agent...\n")
# Step 3: Writer Agent to create report
print("Step 3: Writer Agent creating final report...")
writer_agent = Agent(
system_prompt=(
"You are a Writer Agent that creates clear reports. "
"1. For fact-checks: State whether claims are true or false "
"2. For research: Present key insights in a logical structure "
"3. Keep reports under 500 words with brief source mentions"
),
model=bedrock_model
)
# Execute the Writer Agent with the analysis (output is shown to user)
final_report = writer_agent(
f"Create a report on '{user_input}' based on this analysis:\n\n{analysis}"
)
print("Report creation complete")
# Return the final report
return final_report
if __name__ == "__main__":
# Print welcome message
print("\nAgentic Workflow: Research Assistant\n")
print("This demo shows Strands agents in a workflow with web research.")
print("Try research questions or fact-check claims.")
print("\nExamples:")
print("- \"What are quantum computers?\"")
print("- \"Lemon cures cancer\"")
print("- \"Tuesday comes before Monday in the week\"")
# Interactive loop
while True:
try:
user_input = input("\n> ")
if user_input.lower() == "exit":
print("\nGoodbye!")
break
# Process the input through the workflow of agents
final_report = run_research_workflow(user_input)
except KeyboardInterrupt:
print("\n\nExecution interrupted. Exiting...")
break
except Exception as e:
print(f"\nAn error occurred: {str(e)}")
print("Please try a different request.")
运行这个脚本。
python workflow.py
注意:首次运行这个代码,可能会看到运行中提示npm升级软件包的提示,这是因为Strands Agents调用了http_request这个tool来链接外部互联网,而这个tool是nodejs开发的,因此第一次运行会自动安装对应的库文件,console上可能会提示有npm软件包被安装。
运行后的返回结果如下:
Agentic Workflow: Research Assistant
This demo shows Strands agents in a workflow with web research.
Try research questions or fact-check claims.
Examples:
- "What are quantum computers?"
- "Lemon cures cancer"
- "Tuesday comes before Monday in the week"
> What are quantum computers
Processing: 'What are quantum computers'
Step 1: Researcher Agent gathering web information...
Research complete
Passing research findings to Analyst Agent...
Step 2: Analyst Agent analyzing findings...
Analysis complete
Passing analysis to Writer Agent...
Step 3: Writer Agent creating final report...
# What Are Quantum Computers? Research Report
## Executive Summary
Based on comprehensive analysis, quantum computers represent a revolutionary computing paradigm that harnesses quantum mechanical phenomena to solve specific complex problems far more efficiently than classical computers.
## Core Technology Foundation
Quantum computers operate on four fundamental quantum principles:
- **Superposition**: Quantum bits (qubits) exist in multiple states simultaneously, unlike classical bits that are either 0 or 1
- **Entanglement**: Qubits become interconnected with instantaneous state correlations
- **Interference**: Quantum states can be manipulated to amplify correct answers
- **Decoherence**: The fragile nature of quantum states that requires extreme environmental control
These principles enable quantum computers to process vast amounts of information in parallel, providing exponential computational advantages for specific problem types.
## Current Market Status
The quantum computing industry achieved a significant milestone in 2023 with IBM demonstrating "quantum utility" - practical quantum advantage in real-world applications. This marks the transition from experimental research to early commercial viability.
Industry projections estimate the quantum computing market could reach $450-850 billion by 2035, reflecting substantial growth potential despite current technological limitations.
## Practical Applications
Quantum computers excel in specialized areas including:
- **Molecular simulation** for materials science and chemistry
- **Drug discovery** through complex biological modeling
- **Financial modeling** for risk analysis and optimization
- **Cryptography** and security applications
## Technical Challenges
Current quantum computers require extreme engineering conditions:
- Operation near absolute zero temperatures
- Superconducting materials and specialized hardware
- Sophisticated error correction systems
- Isolation from environmental interference
These requirements make quantum systems complex, expensive, and currently unsuitable for general-purpose computing tasks.
## Key Finding
Quantum computers are specialized problem-solving machines designed to complement, not replace, classical computers. They represent a fundamental shift in computational approach rather than simply faster traditional computing.
**Source**: Analysis based on IBM quantum computing research and industry reports (Reliability: 9/10)Report creation complete
在以上结果中可以看出,用户输入触发了一整个Workflow流程,其中一共有三个Agent被编排,分别是research agent、fact_check agent、report agent。与Swarm模式和Graph模式这两种交互方式所有不同,Workflow模式的起始点是直接注入第一个Agent的,而不需要先构建一个接受人类input的对话agent。由此看到Workflow是精确编排好了的流程,最后对人类的交互反馈集中在编写输出报告的report agent上。
至此,Workflow模式运行成功。
五、小结-设计思路
以上三种模式的Agent交互方式各有特点,适用于不同的场景。再加上本文的上一篇中介绍的Agent as Tool,在A2A交互中共有四种编排模式。它们分别适合:
- Agent as Tool:只启动单一Agent,对外与人类交互体现为唯一的Agent,内部由几个Agent封装为Tool。是否调用到Tool、调用顺序、调用逻辑,由与人类交互的Agent决定
- Agent Swarms:启动多个Agent,松散的编排,Swarm允许它们之间互相协作,协作的机制和原理由接受人类请求作为入口的Agent来协调
- Agent Graphs:像图结构一样的分支,由多条路径,每条路径是预先定义的,最终合并处理结果
- Agent Workflows:人为定义一个Workflow,多个Agent在特定位置依次处理,输入和输出都是明确任务导向
随着生成式AI的发展,未来还会有新的技术和架构诞生,持续关注,Stay tuned。
六、参考资料
Multi-agent Design Patterns¶
Strands Agents Python SDK - Examples Overview
https://github.com/strands-agents/docs/tree/main/docs/examples
最后修改于 2025-09-23